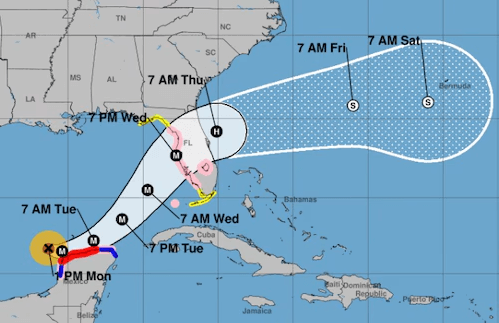
One of the impacts of climate change on transportation logistics is the increase in extreme weather events such as heat waves, droughts, floods, storms, and hurricanes. These events can damage transportation infrastructure such as roads, bridges, railroads, ports, and airports and disrupt the movement of people and goods. For example, in 2017, Hurricane Harvey caused widespread flooding and damage to the transportation network in Texas, impacting supply chains for many industries. In 2019, Cyclone Idai destroyed roads and bridges in Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Malawi, hampering humanitarian relief efforts. GIVE US A CALL FOR A QUOTE (256) 464-2554
Other impacts of climate change on transportation logistics include rising sea levels and increased storm surges, which can threaten coastal transportation infrastructure and increase the risk of coastal erosion and flooding. Sea level rise can also affect inland waterways by altering their depth and width, affecting navigation and freight capacity. For example, a study by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that sea level rise could increase the annual cost of maintaining and repairing U.S. port infrastructure by $1.3 billion to $6.6 billion by 2100.
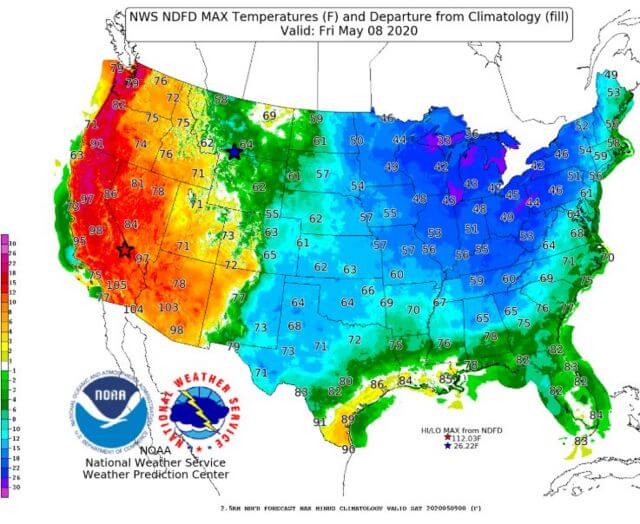
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns also have implications for transportation logistics, which can affect the performance and efficiency of modes and vehicles. Higher temperatures can shorten the life and durability of transportation infrastructure, increase the risk of heat stress for road users and passengers, and affect vehicle fuel efficiency and emissions. Changing precipitation can affect the availability and quality of water resources for modes that rely on water, such as shipping and inland waterways. For example, a BSR study projected that climate change could reduce the navigable length of major rivers in Europe by 6% to 40% by 2050, which would impact freight transport.
To address these impacts of climate change on transport logistics, various adaptation and mitigation measures can be taken. Adaptation measures aim to reduce the vulnerability of transportation systems to climate change impacts and increase their resilience. These include improving the design and maintenance of transportation infrastructure, enhancing emergency preparedness and response capabilities of transportation agencies and authorities, diversifying modes and routes to reduce reliance on single options, and incorporating climate risk assessment and management into transportation planning and decision-making. GIVE US A CALL FOR A QUOTE (256) 464-2554
Transportation Delays: Cold temperatures can affect transportation infrastructure, including roads, railways, and airports. Ice and snow accumulation can lead to hazardous conditions, causing delays and disruptions in the movement of goods. GIVE US A CALL FOR A QUOTE (256) 464-2554
Port Operations: Severe winter weather can impact port operations, affecting the loading and unloading of cargo from ships. Ice accumulation in waterways can impede navigation, leading to delays in the arrival and departure of vessels.
Warehouse Challenges: Cold temperatures can also affect warehouse operations. For example, frozen pipes can cause damage to facilities, and employees may face challenges working in extremely cold conditions, impacting overall efficiency.
Increased Costs: The need for additional resources, such as de-icing agents, increased maintenance of vehicles and equipment, and the use of specialized cold-weather packaging, can contribute to higher operational costs for logistics comp